The Fundamentals of Mixer Settler Technology in Rare Earth Extraction
Design and Components of Mixer Settlers
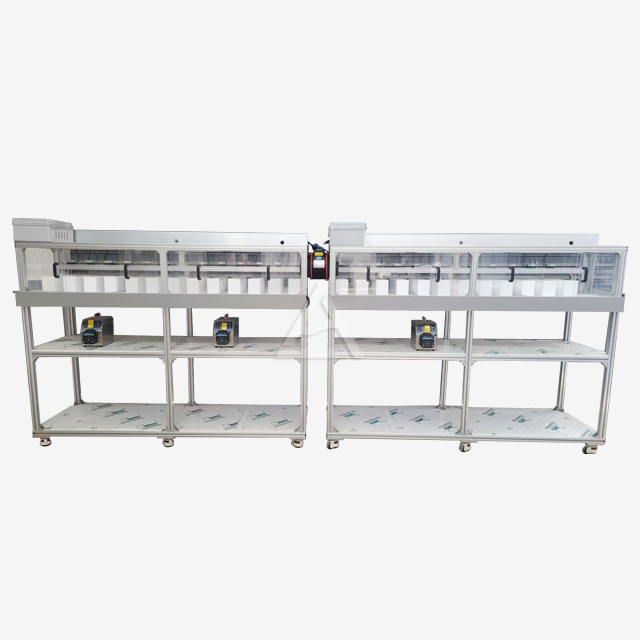
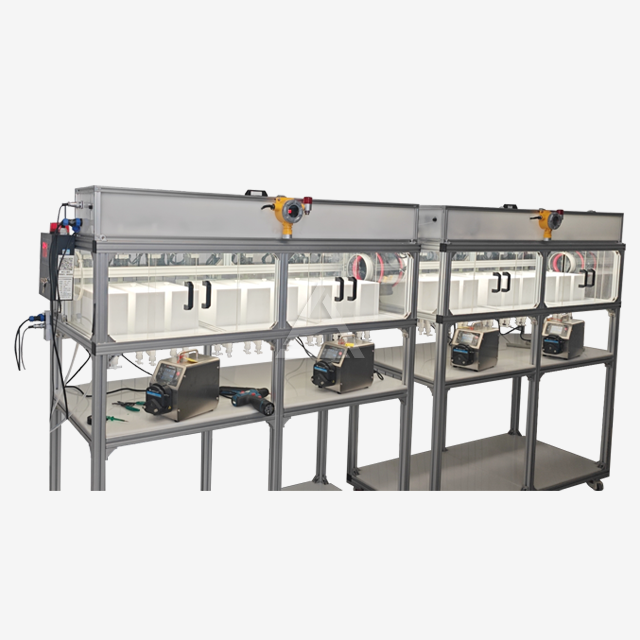
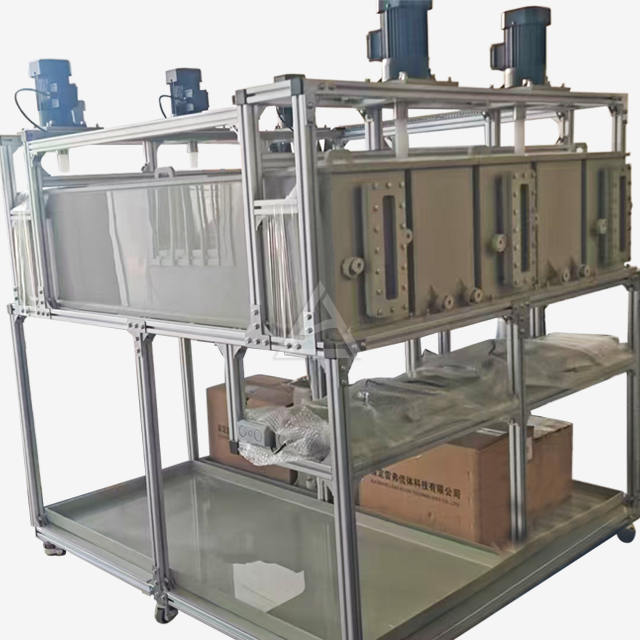
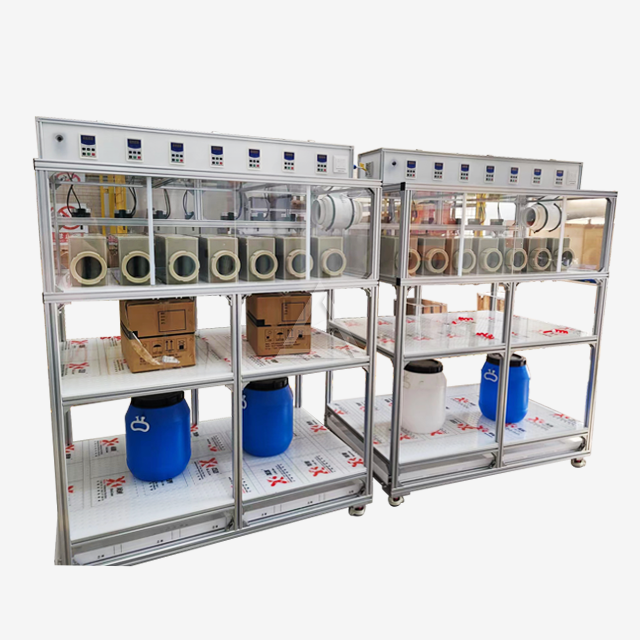
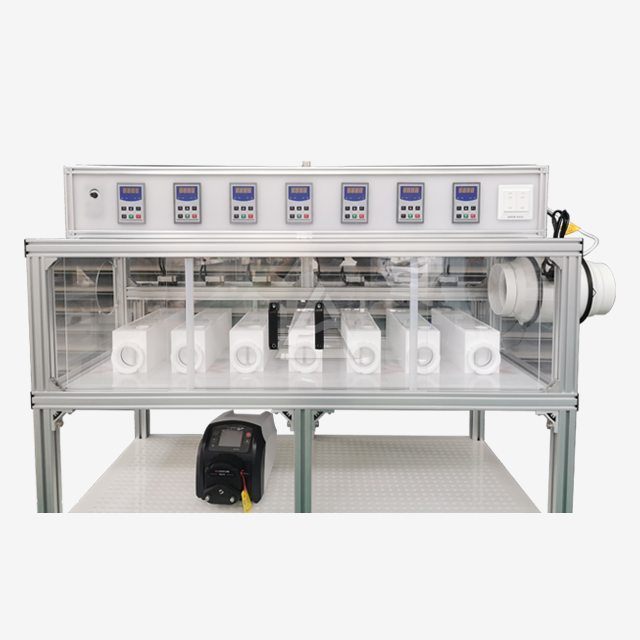
Mixer settlers are ingeniously designed extraction units that consist of two main sections: the mixing chamber and the settling zone. The mixing chamber houses an agitator that vigorously blends the aqueous and organic phases containing rare earth elements. This intense mixing promotes efficient mass transfer between the phases. The settling zone, separated by baffles, allows the mixed phases to separate under gravity. Key components include:
- Agitator: Typically a high-speed impeller that creates turbulent flow for optimal mixing
- Baffles: Strategically placed plates that guide flow and prevent vortex formation
- Weirs: Adjustable overflow barriers that control phase interface heights
- Inlet/outlet ports: Precisely positioned openings for continuous flow operation
The design emphasizes corrosion resistance, with materials like PTFE, PP, or SUS316L chosen based on the chemical environment. Transparent sections made of PMMA allow for real-time monitoring of the extraction process.
Operating Principles and Process Control
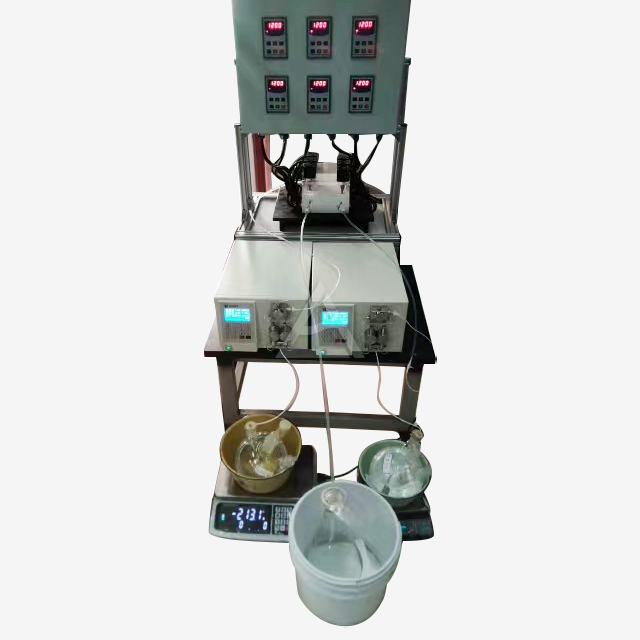
Mixer settlers operate on the principle of liquid-liquid extraction, exploiting differences in solubility between rare earth elements in the aqueous and organic phases. The process involves:
- Feeding: Aqueous feed containing rare earth elements and organic extractant enter separate inlets
- Mixing: The agitator creates a dispersion, maximizing interfacial area for mass transfer
- Settling: The dispersion flows into the quiescent settling zone where phases separate
- Continuous flow: Light and heavy phases exit through respective outlets
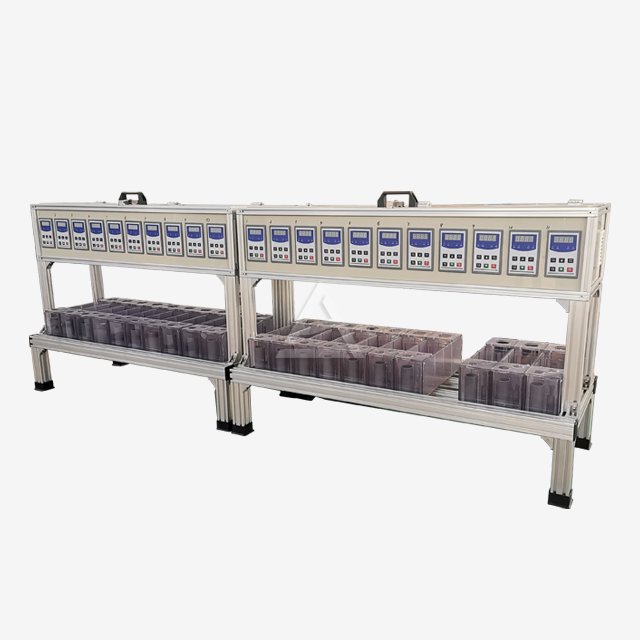
Process control is achieved through adjustable parameters such as agitation speed (100-800 RPM), flow rates, and weir heights. Advanced systems may incorporate pH sensors, temperature control, and PLC integration for precise automation.
Advantages Over Conventional Extraction Methods
Mixer settlers offer several advantages over traditional rare earth extraction techniques:
- Higher efficiency: Improved mass transfer rates due to optimal mixing and large interfacial area
- Flexibility: Easily adjustable operating conditions for different rare earth elements
- Compact footprint: Vertical or horizontal configurations save space compared to mixer-settler tanks
- Scalability: Modular design allows for easy addition or removal of stages
- Reduced chemical consumption: Precise control minimizes extractant and reagent usage
- Lower energy costs: Efficient mixing reduces power requirements by 15-20% compared to conventional systems
These advantages translate to improved rare earth recovery rates, higher product purity, and reduced operational costs.

Optimizing Rare Earth Extraction with Advanced Mixer Settler Techniques
Multi-stage Extraction and Stripping Processes
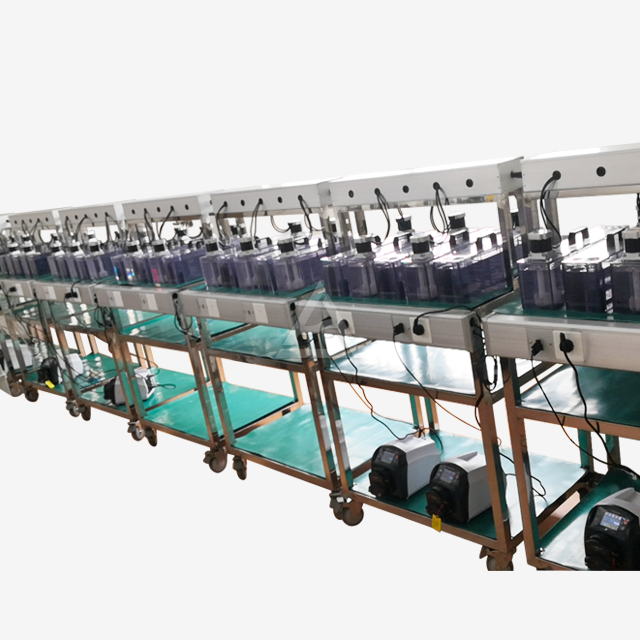
Advanced rare earth extraction often employs multi-stage mixer settler configurations to achieve high purity and recovery rates. This approach involves:
- Extraction stages: Multiple mixer settlers in series progressively remove rare earths from the aqueous feed
- Scrubbing stages: Intermediate steps that selectively remove impurities from the loaded organic phase
- Stripping stages: Reverse extraction process to recover purified rare earths into a new aqueous solution
By carefully designing the number and arrangement of stages, operators can achieve separation of closely related rare earth elements, such as neodymium and praseodymium. The ability to adjust individual stage parameters allows for fine-tuning of the separation process, maximizing efficiency and product quality.
Innovative Mixing Technologies for Enhanced Mass Transfer
Recent advancements in mixer settler design have focused on improving the mixing stage to enhance mass transfer rates. Some innovative approaches include:
- High-shear impellers: Specially designed agitators that create micro-droplets for increased interfacial area
- Pulsed columns: Integration of pulsation devices to create additional turbulence and droplet breakup
- Static mixers: Incorporation of fixed mixing elements to promote uniform dispersion with lower energy input
- Ultrasonic assistance: Application of ultrasonic waves to enhance mass transfer and reduce droplet size
These technologies can significantly reduce mixing times and improve extraction efficiency, particularly for challenging rare earth separations involving elements with similar chemical properties.
Process Intensification and Miniaturization
The drive for more efficient and cost-effective rare earth extraction has led to the development of intensified and miniaturized mixer settler systems. These innovations include:
- Microfluidic extractors: Microscale channels that exploit laminar flow for precise control over interfacial phenomena
- Centrifugal extractors: High-speed rotational devices that combine mixing and settling in a compact unit
- Membrane-assisted extraction: Integration of selective membranes to enhance separation and reduce stage numbers
These intensified processes offer benefits such as reduced solvent inventory, faster kinetics, and improved safety profiles. While currently at various stages of development and implementation, they represent the future direction of rare earth extraction technology.

Environmental and Economic Impacts of Mixer Settler Technology in Rare Earth Processing
Sustainability Advantages of Advanced Extraction Systems
Mixer settler technology contributes significantly to the sustainability of rare earth processing:
- Reduced chemical consumption: Precise control and efficient mass transfer minimize reagent use
- Lower energy requirements: Optimized mixing and compact design reduce power consumption
- Improved water management: Closed-loop systems and efficient separation reduce wastewater generation
- Enhanced recovery rates: Higher efficiency means less waste and more complete utilization of resources
These factors collectively reduce the environmental footprint of rare earth extraction operations, aligning with global sustainability goals and stricter environmental regulations.
Economic Benefits and Return on Investment
The implementation of advanced mixer settler systems offers substantial economic advantages:
- Increased production capacity: Higher throughput and efficiency boost overall output
- Improved product quality: Better separation leads to higher-value rare earth products
- Reduced operating costs: Lower chemical and energy consumption translate to cost savings
- Flexibility in production: Easy reconfiguration allows adaptation to market demands
- Longer equipment lifespan: Corrosion-resistant materials and modular design extend service life
While initial investment may be higher than traditional systems, the long-term benefits often result in attractive returns on investment, particularly for high-value rare earth products.
Future Trends and Technological Developments
The rare earth extraction industry continues to evolve, with several emerging trends in mixer settler technology:
- AI and machine learning integration: Predictive modeling and real-time optimization of extraction processes
- Advanced materials: Development of novel extractants and corrosion-resistant alloys
- Green chemistry approaches: Bio-based solvents and environmentally friendly extraction methods
- Hybrid systems: Combination of mixer settlers with other separation technologies for enhanced performance
These developments promise to further improve the efficiency, sustainability, and economic viability of rare earth extraction processes, ensuring the continued relevance of mixer settler technology in this critical industry.

Conclusion
Mixer settlers have revolutionized rare earth extraction, offering unparalleled efficiency and flexibility. By combining advanced mixing technologies with precise process control, these systems achieve higher recovery rates and product purities while reducing environmental impact. The modular nature of mixer settlers allows for easy scalability and adaptation to diverse rare earth processing needs. As the demand for these critical elements continues to grow, ongoing innovations in mixer settler design and operation will play a crucial role in meeting global rare earth supply challenges sustainably and economically.
Contact Us
Ready to optimize your rare earth extraction process? Cuiyan Technology offers cutting-edge mixer settler solutions tailored to your specific needs. Our expert team can help you design and implement a system that maximizes efficiency, reduces costs, and ensures top-quality rare earth products. Contact us today at wangzhijun@cuiyan-tec.com to discover how our advanced extraction technology can transform your operations.