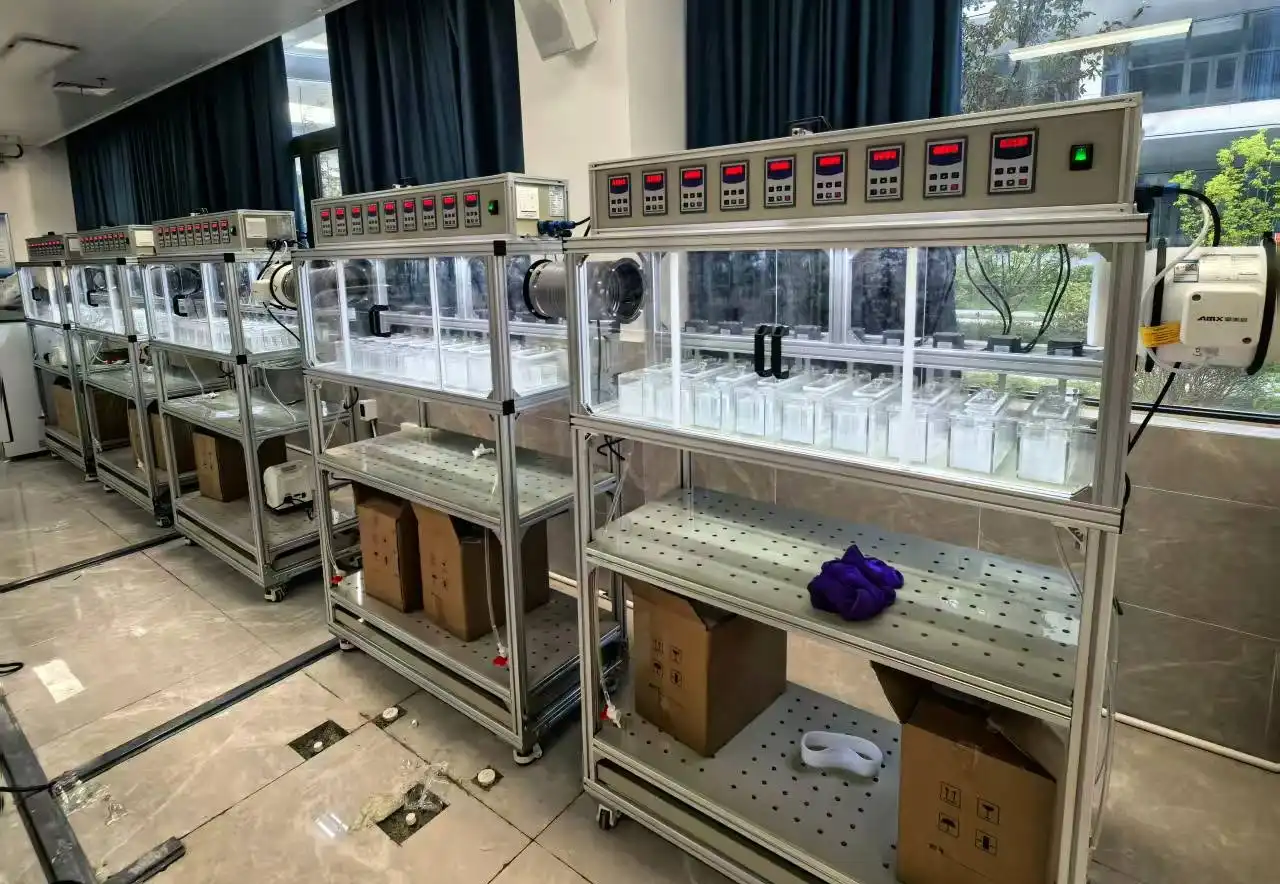
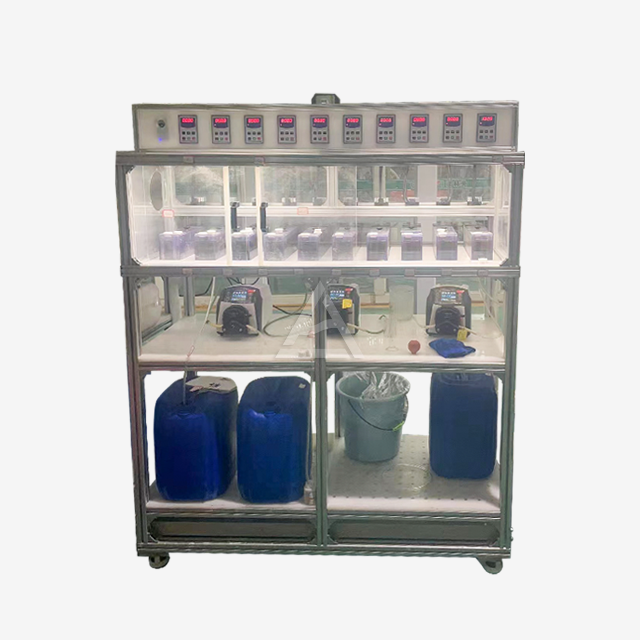
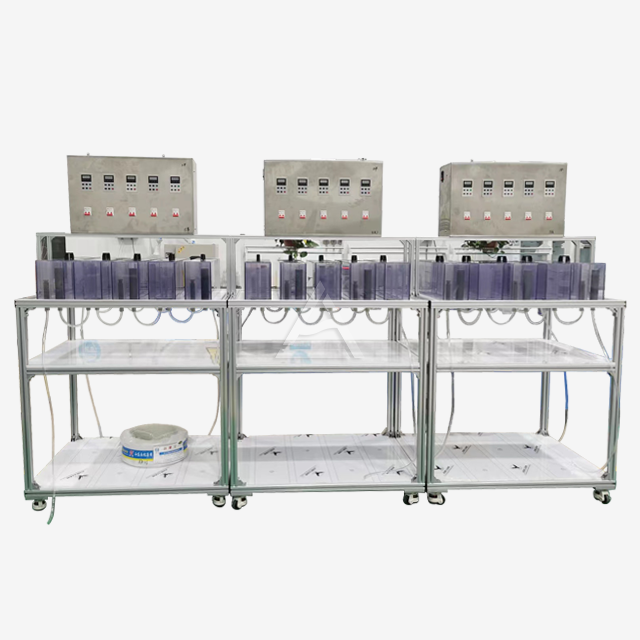
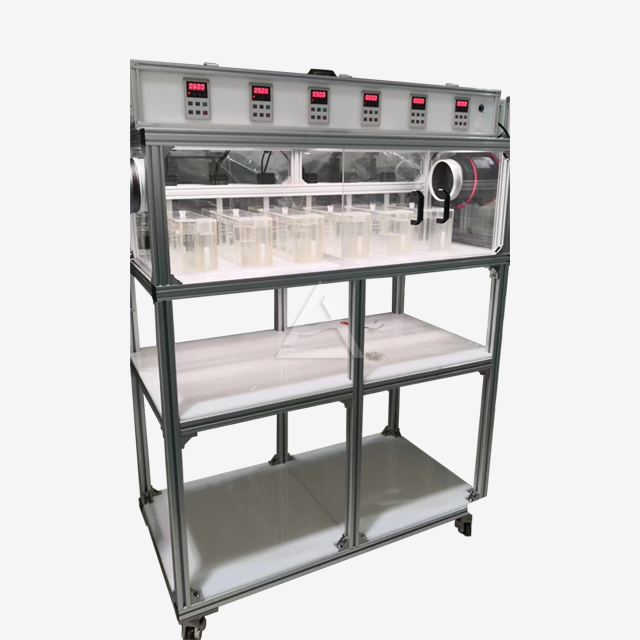
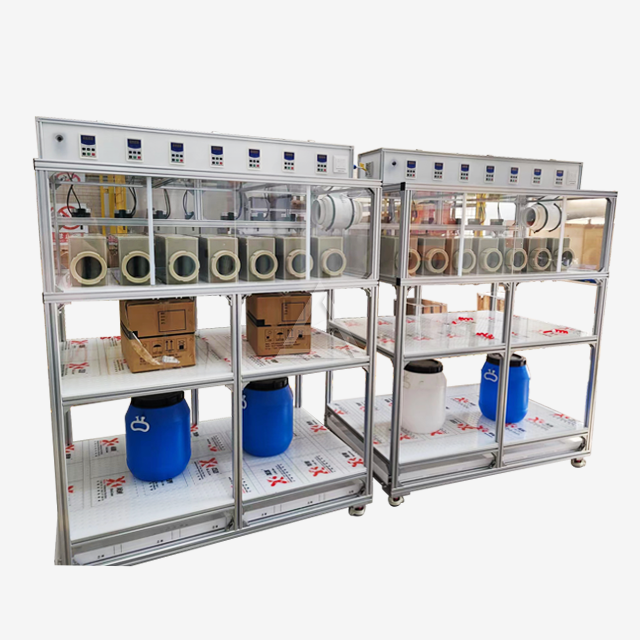
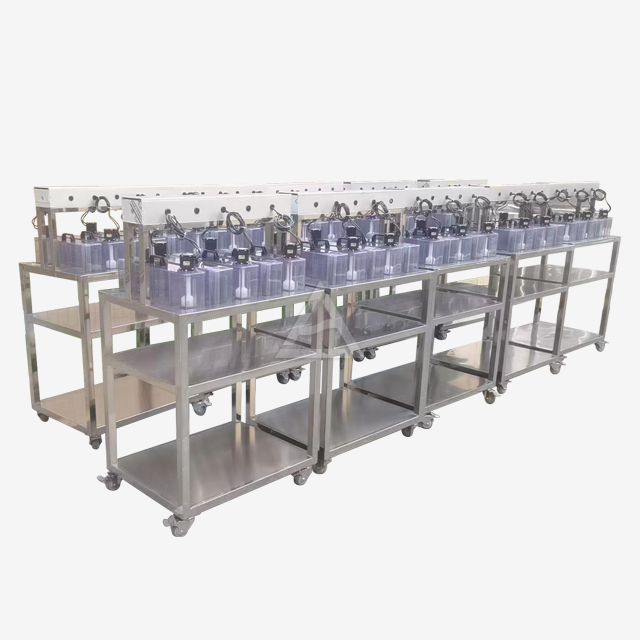
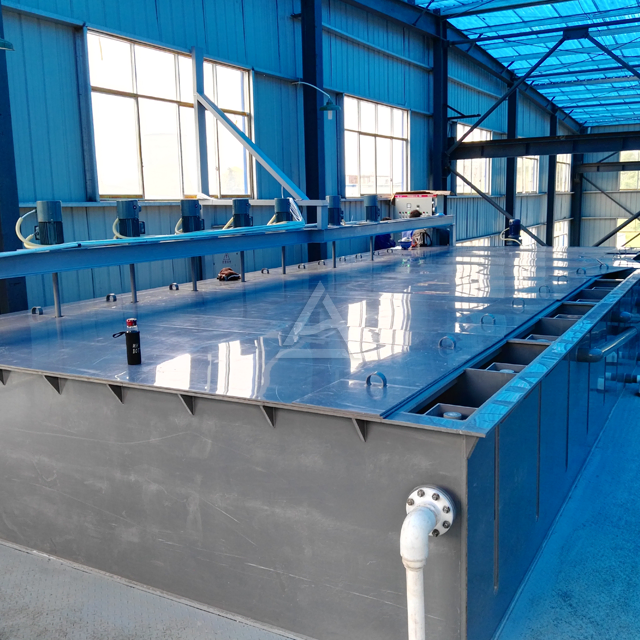
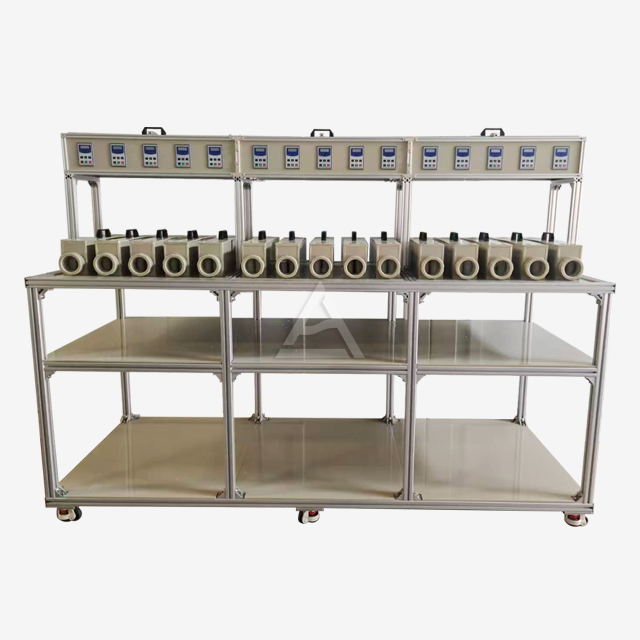
Operational Challenges in Mixer Settler Units
Phase Separation Issues
One of the most frequent problems encountered in mixer settler operations is inadequate phase separation. This can occur due to improper interface control, leading to entrainment of one phase into another. To address this issue, operators should carefully adjust the weir height and monitor the interface level. Implementing a patented baffle design can significantly improve phase separation stability. Additionally, optimizing the settler design by increasing its length or adding coalescence-enhancing elements can promote better phase disengagement.
Emulsion Formation
Excessive emulsion formation can hinder the efficiency of the extraction process. This problem often arises from overaggressive mixing or unsuitable agitator design. To mitigate emulsion issues, consider reducing the agitation speed or modifying the impeller configuration. Implementing a variable-speed drive system allows for fine-tuning of the mixing intensity. In some cases, adding demulsifying agents or adjusting the organic-to-aqueous ratio can help break persistent emulsions.
Flow Rate Imbalances
Maintaining proper flow rates is essential for efficient mixer settler operation. Imbalances can lead to flooding or insufficient contact time between phases. To address this, install flow meters and control valves on both the aqueous and organic feed lines. Implementing a PLC-based control system can help maintain optimal flow ratios and respond to process variations. Regular calibration of pumps and flow control devices is crucial for consistent performance.

Material and Design Considerations for Mixer Settlers
Corrosion and Material Degradation
Chemical compatibility is paramount in mixer settler construction. Corrosion can lead to equipment failure and contamination of process streams. To combat this, select materials appropriate for your specific application. For highly corrosive environments, consider using PTFE-lined or titanium-constructed units. Regular inspections and preventive maintenance, such as applying protective coatings or implementing cathodic protection systems, can extend equipment lifespan.
Seal Integrity and Leakage Prevention
Maintaining seal integrity is crucial for preventing leaks and ensuring environmental safety. High-quality PTFE seals and precision welding techniques can significantly reduce the risk of leakage. Implement a regular seal inspection and replacement program as part of your maintenance routine. For critical applications, consider double mechanical seals or magnetic drive agitators to eliminate shaft seal issues entirely.
Optimizing Mixer Settler Configuration
The configuration of your mixer settler system plays a vital role in its efficiency. Inadequate staging can result in poor extraction performance. Conduct process simulations to determine the optimal number of stages for your specific application. Modular designs allow for easy addition or removal of stages as process requirements change. Consider implementing features like inter-stage sampling ports to monitor extraction efficiency at each step.

Advanced Troubleshooting and Process Optimization
Monitoring and Control Systems
Implementing advanced monitoring and control systems is a critical step in ensuring reliable mixer settler operation. Sensors should be installed to continuously track vital process parameters such as temperature, pH, flow rate, and phase interface level. Integrating these devices with a centralized control platform allows operators to view real-time data and implement automated adjustments when deviations occur. Additionally, predictive analytics powered by machine learning can forecast potential failures or process instabilities, enabling proactive interventions that reduce downtime and improve overall extraction performance.
Enhancing Mass Transfer Efficiency
Optimizing mass transfer efficiency directly impacts the effectiveness of solvent extraction processes. Engineers should evaluate mixing intensity, droplet size distribution, and residence time within the mixer chamber. If performance is limited, alternative impeller designs or the integration of static mixers may be applied to improve phase contact. For systems handling viscous liquids or slow chemical kinetics, pulsed columns and centrifugal contactors offer viable alternatives to conventional mixer settlers. These approaches enhance interfacial area, accelerate equilibrium attainment, and ensure more efficient separation between aqueous and organic phases.
Addressing Scaling and Fouling
Scaling and fouling represent common long-term challenges in mixer settler operations. Deposits of salts, organic residues, or microbial films can restrict flow, reduce mass transfer, and compromise product quality. Preventive strategies include installing Clean-in-Place (CIP) systems to streamline maintenance and minimize downtime. In processes where scaling is prevalent, the application of chemical antiscalants or periodic acid cleaning can effectively mitigate buildup. For biotechnological applications, UV sterilization or targeted chemical treatments may be implemented to inhibit biofilm formation, ensuring consistent equipment performance and prolonging operational life cycles.

Conclusion
Effective troubleshooting and optimization of mixer settler systems are crucial for maintaining high-performance extraction processes. By addressing common issues such as phase separation problems, emulsion formation, and flow imbalances, operators can significantly improve efficiency and reduce downtime. Careful material selection, advanced monitoring systems, and regular maintenance are key to long-term success. As extraction technologies continue to evolve, staying informed about the latest advancements in mixer settler design and operation will be essential for maintaining a competitive edge in various industries.
Contact Us
For expert guidance on optimizing your mixer settler systems, contact Cuiyan Technology. Our team of specialists can provide tailored solutions to enhance your extraction processes, improve efficiency, and reduce operational costs. Reach out to us at wangzhijun@cuiyan-tec.com to discover how our advanced mixer settler technology can transform your operations.