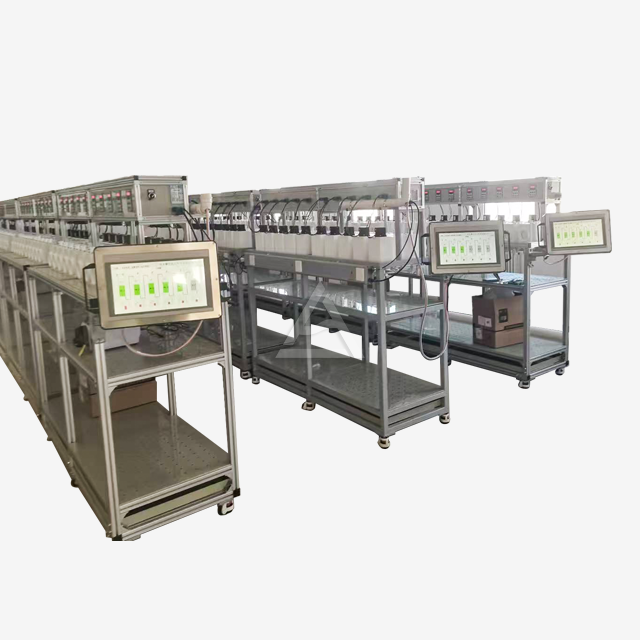
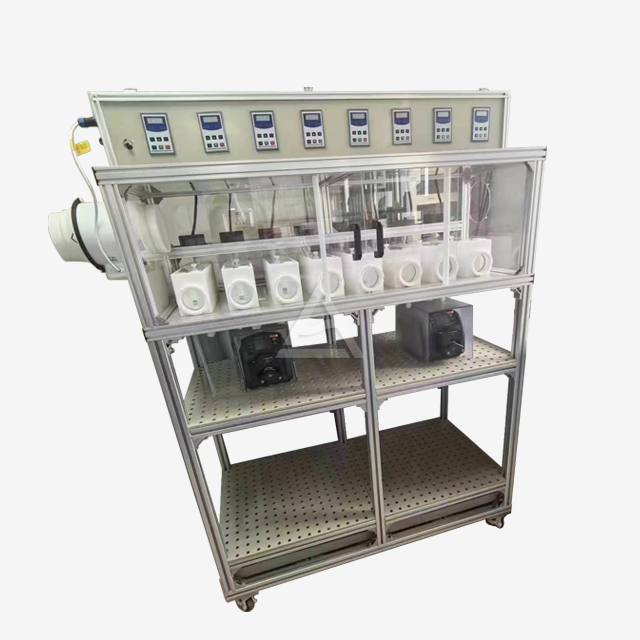
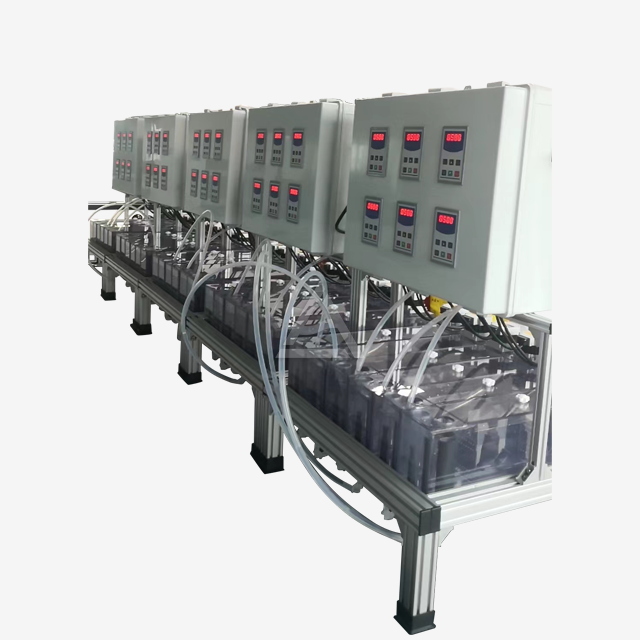
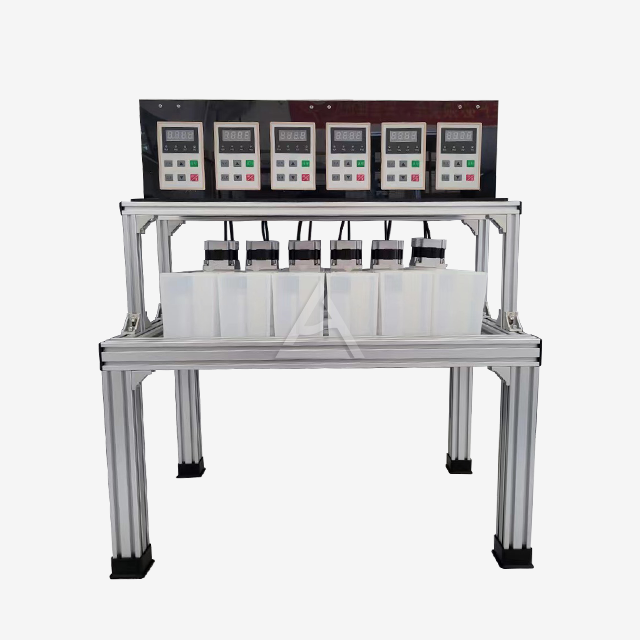
The Role of Mixer Settler in Liquid Liquid Extraction Processes
Mixer settlers play a crucial role in liquid-liquid extraction processes across various industries. These versatile devices combine efficient mixing and phase separation, making them indispensable for extracting valuable compounds from complex mixtures. By utilizing the principles of immiscibility and mass transfer, mixer settlers enable the selective separation of target substances with high precision. Their ability to handle a wide range of flow rates, adjust interface heights, and operate continuously makes them ideal for applications in hydrometallurgy, chemical processing, and environmental remediation. As we delve deeper into the world of mixer settlers, we'll explore their design, functionality, and diverse applications that are shaping modern industrial processes.

Design and Functionality of Mixer Settlers
Structural Components
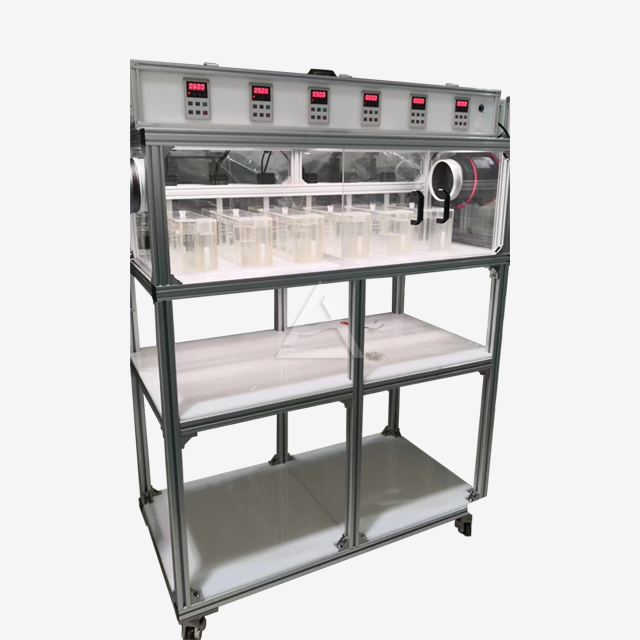
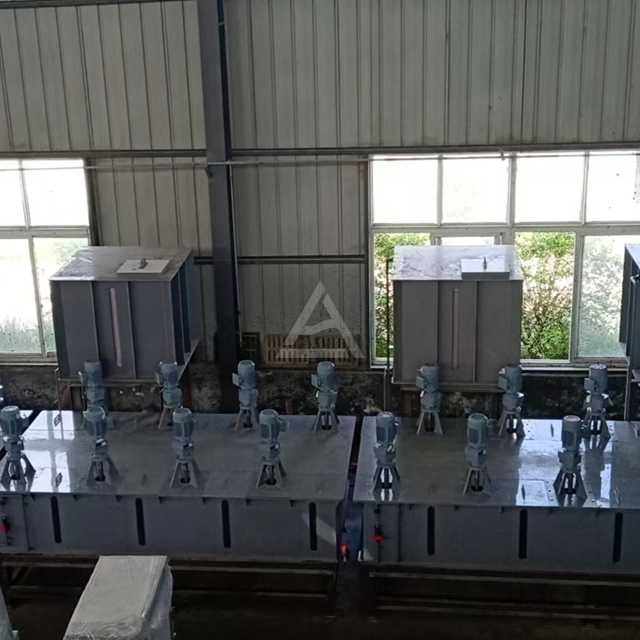
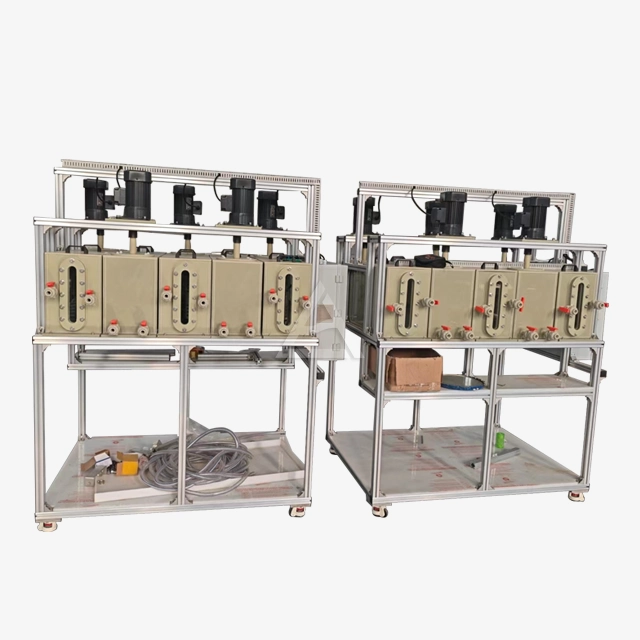
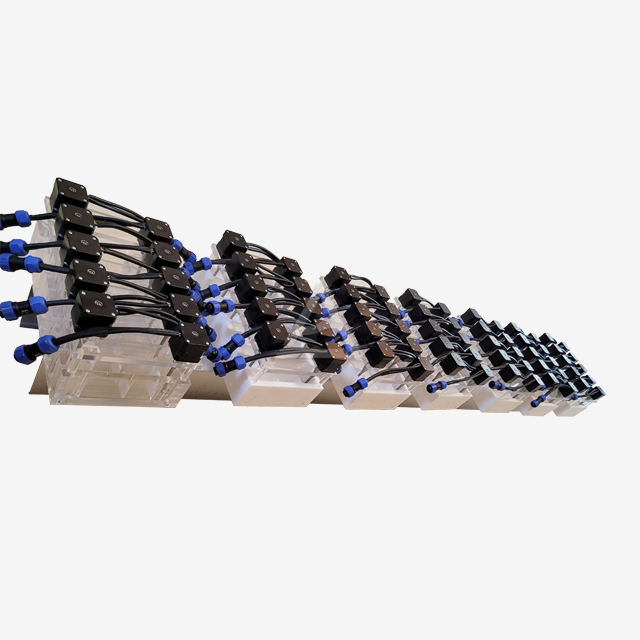
Mixer settlers consist of two primary sections: the mixing chamber and the settling chamber. The mixing chamber houses an agitator that blends the immiscible phases, typically an organic solvent and an aqueous solution. This vigorous mixing creates a large interfacial area, promoting rapid mass transfer between the phases. The settling chamber, separated by a weir, allows the mixed phases to separate under gravity. The design often includes baffles to prevent bubbling and ensure stable phase separation.
Material Selection
The choice of materials for mixer settlers is crucial for their performance and longevity. Corrosion-resistant options like SUS316L stainless steel and PTFE are commonly used to handle acidic or alkaline media with pH ranges from 1 to 14. For processes requiring visual monitoring, transparent materials such as PMMA (acrylic) can be employed for the settling chamber. The selection depends on factors such as chemical compatibility, temperature requirements, and mechanical strength needed for the specific extraction process.
Customization Options
Modern mixer settlers offer a high degree of customization to meet diverse process needs. Manufacturers like Shaanxi Cuiyan Technology Co., Ltd. provide options for varying mixing volumes, from 200ml to 3L or custom sizes. Plate thickness can be adjusted from 5mm to 10mm based on structural requirements. Additional features such as temperature control devices, pH adjustment mechanisms, and water-bath jackets can be integrated to enhance process control and efficiency. The ability to adjust the number of stages, agitator speed, and phase interface height allows for fine-tuning of the extraction process.

Operational Principles and Process Optimization
Mass Transfer Dynamics
The heart of the mixer settler's functionality lies in its ability to facilitate efficient mass transfer between two immiscible liquid phases. As the agitator in the mixing chamber creates a dispersion of droplets, it significantly increases the surface area for mass transfer. The concentration gradient between the two phases drives the transfer of the target compound from one phase to the other. The efficiency of this process depends on factors such as mixing intensity, residence time, and the physical properties of the liquids involved.
Flow Pattern and Phase Separation
After the mixing stage, the dispersion flows into the settling chamber of the mixer settler where gravity takes over. The difference in densities between the two phases causes them to separate, with the lighter phase rising to the top. Carefully designed baffles and weirs guide the flow, ensuring minimal entrainment of one phase in the other. The adjustable weir at the end of the settling chamber allows for precise control of the interface height, which is crucial for maintaining optimal separation efficiency.
Process Control and Optimization
To achieve peak performance, mixer settlers require careful monitoring and adjustment of several parameters. Modern units often incorporate sensor integration, allowing for real-time tracking of pH, temperature, and liquid levels via PLC systems. This data enables operators to make informed decisions about agitation speed (typically adjustable from 100 to 800 RPM), flow rates, and phase ratios. By fine-tuning these variables, it's possible to optimize extraction efficiency, minimize solvent loss, and reduce energy consumption by 15-20% compared to traditional extraction methods.

Applications and Industry Impact
Rare Earth Element Extraction
The extraction of rare earth elements like neodymium and dysprosium has become increasingly important in the technology sector. Mixer settlers excel in this application due to their ability to handle the complex multi-stage extraction processes required. The equipment's resistance to corrosive media and precise control over phase separation make it ideal for separating these valuable elements from ore concentrates. By enabling efficient purification of rare earth elements, mixer settlers contribute to the production of high-performance magnets used in electric vehicles and advanced electronics, supporting the growth of sustainable technologies.
Battery Recycling and Metal Recovery
As the demand for electric vehicles grows, so does the need for efficient battery recycling processes. Mixer settlers play a pivotal role in recovering critical materials like lithium and cobalt from spent batteries. The extraction process typically involves leaching the battery materials with acids, followed by a series of solvent extraction steps in mixer settlers. This method allows for selective separation of different metals, with each stage optimized for a specific element. The recovered materials can then be reused in new battery production, creating a more sustainable lifecycle for energy storage technologies.
Nuclear Fuel Processing
In the nuclear industry, mixer settlers are indispensable for the separation of uranium and plutonium in fuel reprocessing. The equipment's ability to handle radioactive materials safely, coupled with its high extraction efficiency, makes it suitable for this sensitive application. Multiple stages of mixer settlers are often employed to achieve the required purity levels, with each stage carefully controlled to prevent cross-contamination. This application showcases the versatility of mixer settlers in handling complex, high-stakes separation processes that are crucial for energy production and nuclear non-proliferation efforts.

Conclusion
Mixer settlers have emerged as a cornerstone technology in liquid-liquid extraction processes, offering unparalleled flexibility and efficiency across a wide range of industries. Their ability to combine intense mixing with controlled separation makes them invaluable for applications ranging from rare earth element purification to nuclear fuel processing. As industries continue to seek more sustainable and efficient extraction methods, the role of mixer settlers is likely to expand further, driven by ongoing innovations in design and process control. By enabling the recovery of valuable resources and facilitating cleaner production processes, mixer settlers are not just shaping industrial practices but also contributing to a more sustainable future.
Contact Us
Ready to optimize your extraction processes? Cuiyan Technology offers cutting-edge mixer settler solutions tailored to your specific needs. Experience increased efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and superior separation quality. Contact us at wangzhijun@cuiyan-tec.com to discover how our expertise can transform your operations.
References
1. Smith, J.K. (2021). Advances in Liquid-Liquid Extraction Technology: The Rise of Mixer Settlers. Journal of Chemical Engineering Progress, 117(5), 45-52.
2. Zhang, L., & Chen, X. (2020). Optimization of Rare Earth Element Extraction Using Advanced Mixer Settler Designs. Hydrometallurgy, 195, 105380.
3. Johnson, R.M., et al. (2019). Energy-Efficient Metal Recovery from Li-ion Batteries: A Comparative Study of Mixer Settler and Centrifugal Extractor Technologies. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 148, 136-144.
4. Nakamura, T., & Sato, Y. (2022). Nuclear Fuel Reprocessing: Advancements in Mixer Settler Applications for Uranium and Plutonium Separation. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 144, 103961.
5. Brown, A.E. (2018). Material Selection Criteria for Mixer Settlers in Corrosive Environments. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 138, 248-259.
6. Lee, H.S., & Park, K.H. (2023). Process Intensification in Liquid-Liquid Extraction: A Review of Modern Mixer Settler Designs and Control Strategies. Separation and Purification Technology, 303, 122289.